Overactive Bladder Interrupting your life?
Christopher Tornehl, MD
Urology
Western Wisconsin Urology
Eau Claire
Do you have a difficulty in meetings or events because you feel the frequent strong urge to go to the bathroom? Do you worry you won’t make it to the bathroom in time and will have embarrassing accidents? If so, you may be among the 10% of Americans who have overactive bladder.
“Overactive bladder is a common, aggravating and treatable condition.”
The bladder’s function is to store urine, expanding like a balloon until full, at which point we sense the need to go to the bathroom. People with overactive bladder may suffer from involuntary contractions of bladder muscles or increased sensitivity to the bladder filling with urine. This leads to extreme urgency to use the bathroom, increased urinary frequency, urine leakage, and leads many sufferers of overactive bladder to avoid public places or social functions. The condition is more common in the elderly and can contribute to depression.
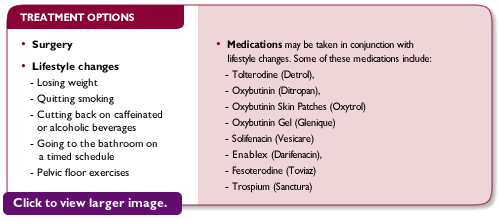
Many medications for overactive bladder are currently on the market. They are designed to relax the bladder and decrease the sensation of urgency when urinating. While most people will experience some degree of relief of their overactive bladder with medications, common side effects include dry mouth and constipation. Behavioral changes and medications are the first step towards treatment of overactive bladder.
When medications and behavioral changes fail to bring significant improvement, surgical procedures are an option.
Botox injection into the bladder helps relax the bladder muscle curbing urinary urgency, frequency and leakage. Botox generally brings relief for about six months before effects wear off. This is a relatively new approach to overactive bladder and long-term studies have not been completed on the use of botox for overactive bladder. Another surgical option involves stripping the bladder of its muscle. While effective for many patients, this is a rather invasive approach to treatment of overactive bladder. Finally, a nerve stimulator known as Interstim can be placed in the low back. This device sends stimulation to the nerves that play a role in the bladder’s function. Interstim brings relief to roughly 70% of people who fail to respond to medications or cannot tolerate the side effects of medications. Interstim usage across the country has been growing rapidly due to its effectiveness and requires only an outpatient procedure for implantation.

Effective treatment for overactive bladder helps people reclaim control of their lives whether at work, the mall, out to eat with friends, or driving around town.
A number of safe, effective options exist whether changing habits, using medications, or even undergoing surgery. Please call Western Wisconsin Urology if you are interested in discussing these
treatment options further.
Dr. Christopher Tornehl – Western Wisconsin Urology
For information or to schedule an appointment:
715-835-6548 | www.eauclaireurology.com
Dr. Tornehl sees patients in Eau Claire, Amery, New Richmond, Menomonie and Shell Lake.




 © 2009 OakLeaf Medical Network and OakLeaf Surgical Hospital. All rights reserved.
© 2009 OakLeaf Medical Network and OakLeaf Surgical Hospital. All rights reserved.